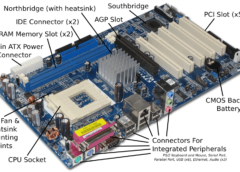
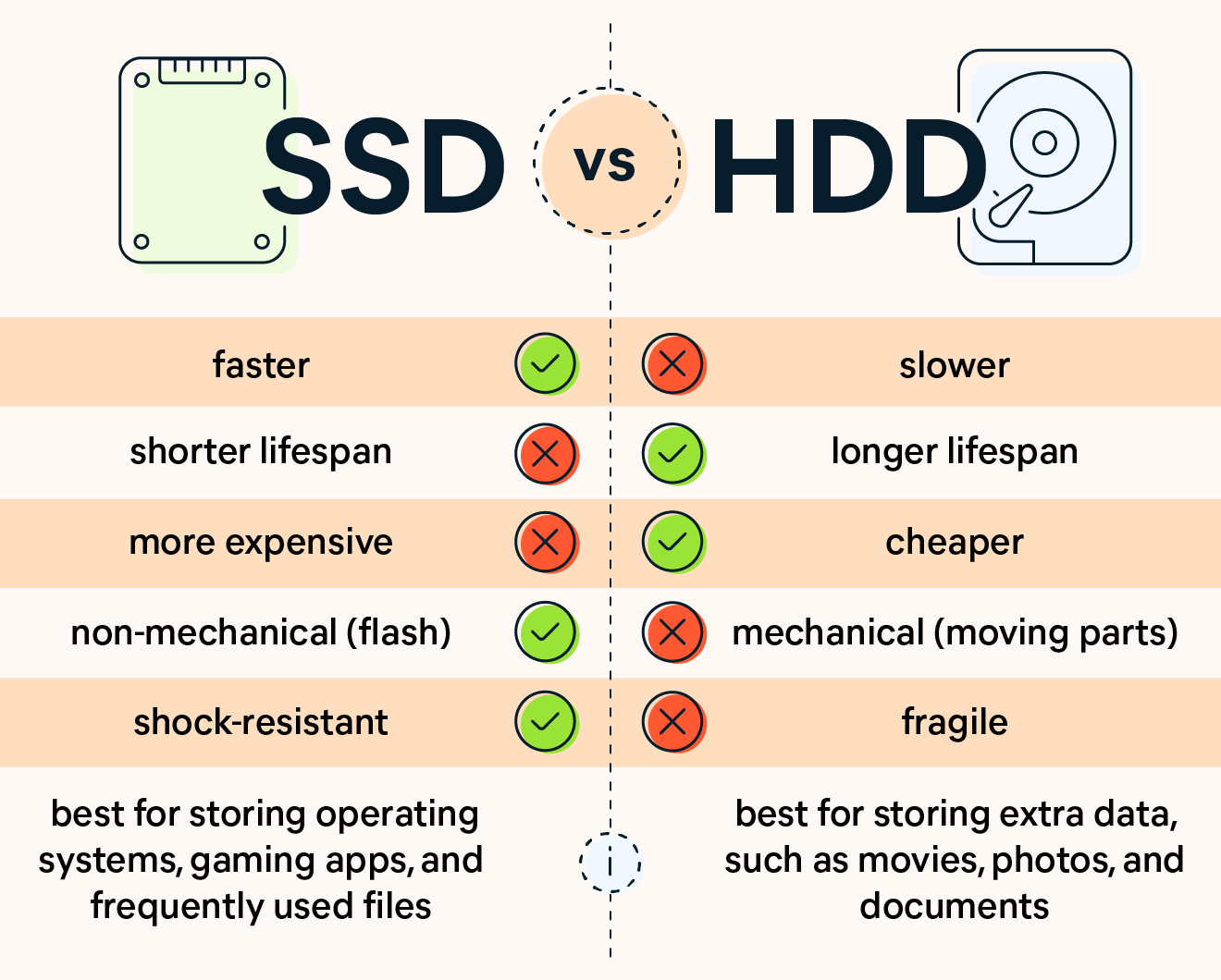
When comparing NVMe storage, SSD (SATA SSD), and HDD, each has distinct characteristics, performance levels, and ideal use cases. Here’s a breakdown of these three types of storage:
1. HDD (Hard Disk Drive)
- Technology: Utilizes spinning magnetic disks (platters) to store data. A mechanical arm moves to read or write data on the disk.
- Speed:
- Read/Write Speeds: Typically around 100-150 MB/s.
- Latency: Higher due to the mechanical parts; delays are caused by the time it takes for the disk to spin and the read/write heads to move to the correct location.
- Capacity: Common capacities range from 500GB to several terabytes (TB). Generally offers the most storage space for the cost.
- Durability: More prone to failure due to mechanical parts. Sensitive to physical shock and vibration.
- Cost: The most cost-effective in terms of price per GB.
- Use Cases: Ideal for bulk storage, backups, media libraries, and situations where cost and capacity are more important than speed.
2. SSD (Solid State Drive) – SATA SSD
- Technology: Uses NAND flash memory to store data, with no moving parts. SATA (Serial ATA) is the interface used to connect the SSD to the computer.
- Speed:
- Read/Write Speeds: Typically around 500-600 MB/s, limited by the SATA interface.
- Latency: Lower than HDDs, providing faster data access and improved performance in tasks like booting up and loading applications.
- Capacity: Common capacities range from 120GB to 4TB. Prices are higher than HDDs but have been decreasing over time.
- Durability: More durable than HDDs due to the absence of moving parts. Resistant to physical shock and vibration.
- Cost: More expensive than HDDs but cheaper than NVMe SSDs in terms of price per GB.
- Use Cases: Suitable for operating systems, applications, and gaming where faster access times and reliability are important.
3. NVMe Storage (NVMe SSD)
- Technology: Uses NAND flash memory, like SATA SSDs, but connects via the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) interface, which offers much higher bandwidth. NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is the protocol used, optimized for the faster PCIe interface.
- Speed:
- Read/Write Speeds: Typically between 2000 MB/s to 7000 MB/s or higher, depending on the specific NVMe drive and the PCIe generation (e.g., PCIe 3.0, 4.0, or 5.0).
- Latency: Extremely low, making it the fastest storage option available, with near-instant access times.
- Capacity: Common capacities range from 256GB to 4TB. While prices have been decreasing, NVMe SSDs are still more expensive than SATA SSDs and HDDs.
- Durability: As durable as SATA SSDs, with no moving parts.
- Cost: The most expensive in terms of price per GB but offers unparalleled performance.
- Use Cases: Best for high-performance computing, gaming, professional video editing, data-intensive tasks, and any application where maximum speed is crucial.
Summary:
- HDD: Best for cost-effective, high-capacity storage when speed is not critical.
- SATA SSD: Offers a balance of speed, durability, and capacity, making it ideal for most general computing needs.
- NVMe SSD: The fastest and most responsive storage option, ideal for users who need top-tier performance for demanding tasks.
Choosing between these options depends on your specific needs, such as whether you prioritize speed, storage capacity, or cost.
![]()









![[Resource]: Installing Webuzo on Your Nestict Cloud VPS: A Detailed Guide](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/image.webp)
![[Resource] : Comprehensive List of Equity Bank Codes Across Kenya by Region](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/image-5.png)


![[Continuation]: Current Challenges in Making Physics and Geography Compulsory](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/The-universe-of-mathematics-physic-and-astronomy-its-ama…-Flickr.jpg)
![[Resource] : Why Physics and Geography Should Be Compulsory Like Mathematics in Education](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/image.png)
![[LINKTREE] 2024 PAST PAPERS , NOTES ,RESOURCE,REVISION,EXAMINATIONS](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/SCHM.jpeg)


![Maritime Terms, Abbreviations and Acronyms [Shipping Terms – Searchable]](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/Container-Stowage-Stock-Illustrations-–-71-Container-Stowage-Stock-Illustrations-Vectors-Clipart-Dreamstime.jpg)
![Maritime Terms, Abbreviations and Acronyms [ Shipping Terms]](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/image.png)










![[Updated 2024] – Passport Application FOR CHILDREN ONLY(PERSONS UNDER 18 YEARS)](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/keppp-240x172.png)
![[Updated 2024] -Passport Application FOR ADULTS ONLY-PERSONS OVER 18 YEARS](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/EAF-Passport-e1631045054464-400x800-1-240x172.jpg)