1. Situation: Climate Change and Global Warming
Problem: Rising global temperatures, melting polar ice caps, and extreme weather events are wreaking havoc on ecosystems and human communities. Many people lack a clear understanding of climate systems and their role in mitigating climate change.
Solution Through Physics and Geography:
- Physics: Teaches the science behind greenhouse gases, energy transfer, and renewable energy technologies like solar panels and wind turbines.
- Geography: Provides insights into the geographic impacts of climate change, such as desertification, rising sea levels, and migration patterns.
- Outcome:
- A generation educated in climate systems and renewable energy could drive global efforts to adopt sustainable energy solutions.
- Improved policies for urban planning, agriculture, and disaster management based on geographical data and scientific analysis.
2. Situation: Natural Disasters and Poor Preparedness
Problem: Earthquakes, floods, hurricanes, and wildfires cause loss of life and property. In many cases, the damage is exacerbated by poor understanding and preparation.
Solution Through Physics and Geography:
- Physics: Explains the mechanics of earthquakes, weather patterns, and the physics of tsunamis. It also helps design disaster-resilient structures.
- Geography: Teaches mapping techniques, risk assessment, and planning for vulnerable areas.
- Outcome:
- Improved early warning systems using geographical data and physical principles.
- Educated communities that can respond effectively to disasters, reducing casualties and damage.
- Urban centers built with earthquake-resistant infrastructure and flood management systems.
3. Situation: Energy Crisis and Overdependence on Fossil Fuels
Problem: Fossil fuels are depleting, and their excessive use is driving environmental pollution. Many people are unaware of renewable energy options or how to use energy efficiently.
Solution Through Physics and Geography:
- Physics: Educates about energy conservation, the physics of wind and solar power, and nuclear fusion.
- Geography: Identifies regions suitable for renewable energy installations, such as areas with high solar intensity or consistent winds.
- Outcome:
- Wider adoption of renewable energy solutions like solar farms and wind turbines in suitable locations.
- Reduction in carbon emissions and energy costs through efficient resource utilization.
4. Situation: Rapid Urbanization and Poor City Planning
Problem: Unplanned urban sprawl leads to traffic congestion, pollution, and inadequate infrastructure, making cities unsustainable.
Solution Through Physics and Geography:
- Physics: Helps optimize transportation systems using principles of mechanics and energy efficiency. Physics also aids in water and waste management solutions.
- Geography: Informs urban planning by analyzing population distribution, land use, and resource availability.
- Outcome:
- Smart cities designed with efficient transport systems, green spaces, and sustainable resource management.
- Reduction in urban pollution and better quality of life for city dwellers.
5. Situation: Resource Conflicts and Inequality
Problem: Disputes over water, minerals, and agricultural land are common, often fueled by ignorance of resource distribution and sustainability.
Solution Through Physics and Geography:
- Physics: Offers technologies for resource extraction and management, such as water desalination or mineral recycling.
- Geography: Maps resource availability, ensuring equitable and sustainable distribution.
- Outcome:
- Efficient use of natural resources, reducing conflicts over scarcity.
- Better agricultural practices tailored to local soil and climatic conditions, addressing food insecurity.
Tabulated global index rankings per continent
Here is a tabulated representation of global index rankings related to the challenges discussed (climate change, natural disasters, energy crisis, urbanization, and resource inequality) across continents:
|
Continent |
Climate Change Vulnerability |
Natural Disaster Risk Index |
Energy Transition Readiness |
Urbanization Quality Index |
Resource Inequality Index |
|
Africa |
Highly vulnerable (e.g., Chad, Sudan) |
High risk (e.g., Mozambique, Somalia) |
Low readiness (e.g., Nigeria, Kenya) |
Low urban quality (e.g., Lagos, Kinshasa) |
High inequality (e.g., South Africa) |
|
Asia |
Moderate vulnerability (e.g., India, Bangladesh) |
High risk (e.g., Philippines, Japan) |
Varies: High in Japan, low in Bangladesh |
Varies widely (e.g., Singapore high) |
Resource conflicts in Central Asia |
|
Europe |
Low vulnerability (e.g., Norway, Finland) |
Low risk (e.g., Germany, Switzerland) |
High readiness (e.g., Denmark, Sweden) |
High urban quality (e.g., Copenhagen) |
Low inequality (e.g., Nordic nations) |
|
North America |
Moderate (e.g., USA) |
Moderate risk (e.g., USA, Mexico) |
High readiness (e.g., USA, Canada) |
High urban quality (e.g., Toronto) |
Moderate inequality (e.g., USA) |
|
South America |
High vulnerability (e.g., Brazil, Bolivia) |
Moderate risk (e.g., Chile, Colombia) |
Low readiness (e.g., Venezuela, Bolivia) |
Moderate urban quality (e.g., Chile) |
High inequality (e.g., Brazil) |
|
Oceania |
Moderate vulnerability (e.g., Australia, Fiji) |
High risk (e.g., Pacific Islands) |
High readiness (e.g., Australia) |
High urban quality (e.g., Sydney) |
Low inequality (e.g., New Zealand) |
Insights by Challenge
- Climate Change Vulnerability: Africa and South America face high exposure due to poor adaptive capacity. Europe leads in mitigation efforts due to better policies and technologies
- Natural Disaster Risk: Island nations in Asia and Oceania are most prone to disasters. Urban planning in Europe and North America reduces risk
- Energy Crisis Readiness: Developed regions (e.g., Europe, Oceania) excel in transitioning to renewable energy, while Africa and South America lag due to financial and infrastructural gaps
- Urbanization Quality: European cities dominate quality indexes due to efficient governance. Rapidly growing cities in Asia and Africa face challenges like congestion and inadequate housing.
- Resource Inequality: Africa and South America struggle with unequal distribution of resources, while Nordic countries in Europe maintain equitable systems
Tabulated learning index and performance between south korea, Germany and Singapore education systems and policies and their benefits
Comparative Analysis of Education Systems in South Korea, Germany, and Singapore
|
Aspect |
South Korea |
Germany |
Singapore |
|
Learning Index |
Highly focused on memorization and test performance. Students spend significant hours studying, often supplemented by private tuition |
Emphasis on critical thinking and vocational training. Dual education system combines academic and hands-on experience |
Blends rigorous academics with a strong focus on STEM. Recognized for top rankings in reading, science, and math globally |
|
Teaching Policies |
Teachers are well-respected with high job security and rigorous training requirements. Technology integration is widespread . |
Teachers are highly trained. Emphasis on teacher autonomy, enabling creative and tailored instruction . |
Teachers receive strong government support and frequent professional development. Pedagogical approaches evolve to meet global standards . |
|
Performance (PISA) |
Consistently ranks in the top 5 globally, excelling in math and science. Students are high achievers but face intense pressure . |
PISA scores show strong performance, though there has been a recent decline due to systemic challenges and pandemic disruptions . |
Leads globally, often surpassing others in reading, math, and science. Students are years ahead compared to peers worldwide . |
|
Education Philosophy |
Success-oriented with a focus on discipline and results. Prioritizes entrance exams to prestigious universities . |
Values balance, with equal weight on academic and vocational pathways. Encourages lifelong learning . |
Emphasizes applied knowledge and innovation. The system evolves with emerging economic needs, producing globally competitive graduates . |
|
Benefits |
Produces high-performing students with exceptional discipline. Prepares students well for competitive academic and career pursuits . |
Nurtures skilled professionals through its vocational training system. Encourages self-reliance and adaptability |
Graduates excel in global STEM fields, contributing to economic growth. The system is admired for fostering early proficiency in key subjects . |
![]()









![[Resource]: Installing Webuzo on Your Nestict Cloud VPS: A Detailed Guide](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/image.webp)
![[Resource] : Comprehensive List of Equity Bank Codes Across Kenya by Region](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/image-5.png)

![[Continuation]: Current Challenges in Making Physics and Geography Compulsory](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/The-universe-of-mathematics-physic-and-astronomy-its-ama…-Flickr.jpg)
![[Resource] : Why Physics and Geography Should Be Compulsory Like Mathematics in Education](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/image.png)
![[LINKTREE] 2024 PAST PAPERS , NOTES ,RESOURCE,REVISION,EXAMINATIONS](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/SCHM.jpeg)


![Maritime Terms, Abbreviations and Acronyms [Shipping Terms – Searchable]](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/Container-Stowage-Stock-Illustrations-–-71-Container-Stowage-Stock-Illustrations-Vectors-Clipart-Dreamstime.jpg)
![Maritime Terms, Abbreviations and Acronyms [ Shipping Terms]](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/image.png)




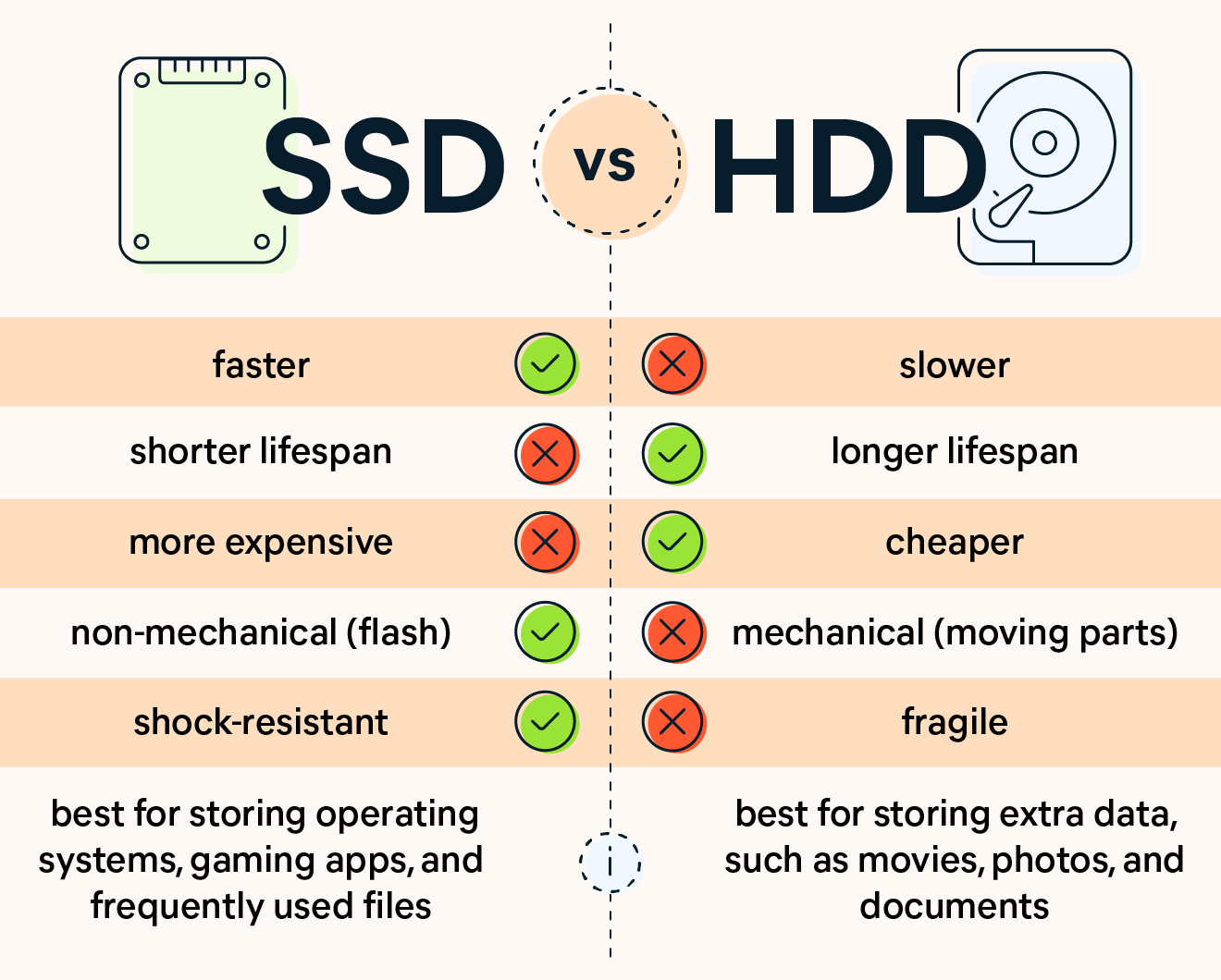
![[Explainer]: NVMe storage, SSD (SATA SSD), and HDD](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Laptops-are-available-with-SSDs-and-HDDs.png)






![[Updated 2024] – Passport Application FOR CHILDREN ONLY(PERSONS UNDER 18 YEARS)](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/keppp-240x172.png)
![[Updated 2024] -Passport Application FOR ADULTS ONLY-PERSONS OVER 18 YEARS](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/EAF-Passport-e1631045054464-400x800-1-240x172.jpg)