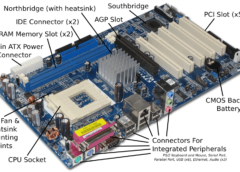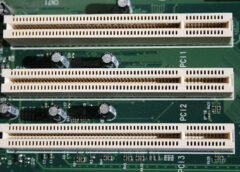
The function of the PCI slot is to allow you expand computer capabilities. PCI stands for Peripheral Component Interconnect. This is a computer slot that allows you to insert expansion cards into your computer. These can come in the form of sound cards, RAID cards, SSDs, graphics cards, NIC cards, Co-processors, and several other functional computer parts. So it enables you to expand the capabilities of the PC by adding what you do not have. It falls under the expansion bus category also known as the I/O bus. Other names for the I/O apart from expansion bus include, “external bus” or “host bus”.
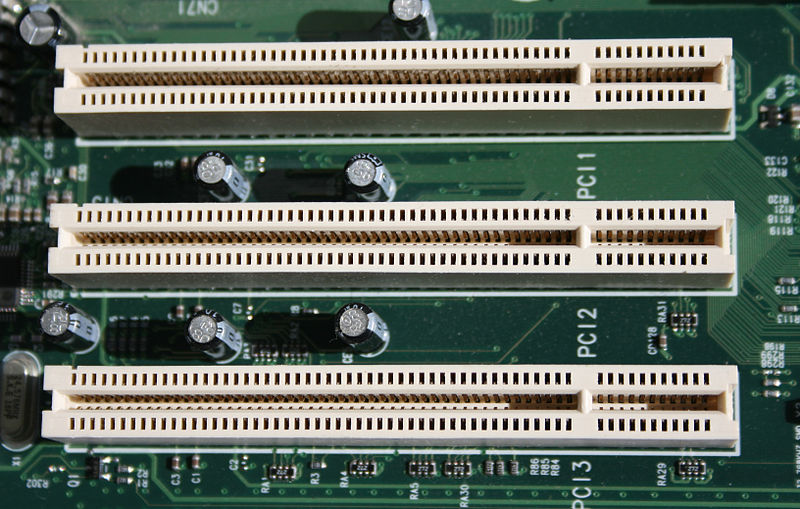
The Expansion Bus
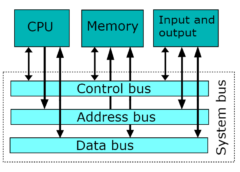
An expansion bus is an input/output pathway from the CPU to peripheral devices. It is made up of a series of slots on the motherboard. Expansion boards (cards) plug into the bus. PCI is the most common expansion bus in a PC and other hardware platforms. Buses carry signals such as data, memory addresses, power, and control signals from component to component.
Expansion buses enhance the PC’s capabilities by allowing users to add missing features in their computers by slotting adapter cards into expansion slots.
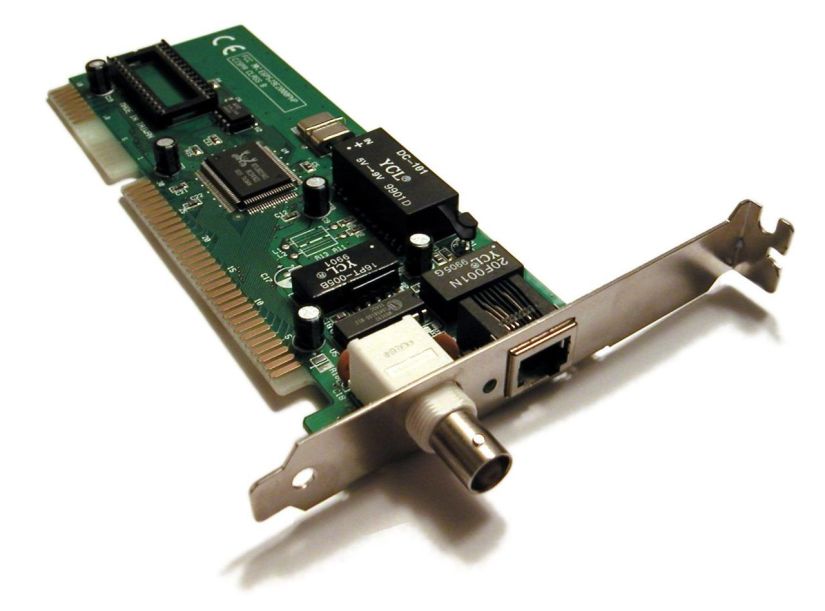
Expansion Bus Types
Common expansion bus types found on computers:
- ISA – Industry Standard Architecture
- EISA – Extended Industry Standard Architecture
- MCA – Micro Channel Architecture
- VESA – Video Electronics Standards Association
- PCI – Peripheral Component Interconnect
- PCI Express (PCI-X) – Peripheral Component Interconnect Express
- PCMCIA – Personal Computer Memory Card Industry Association (Also called PC bus)
- AGP – Accelerated Graphics Port
- SCSI – Small Computer Systems Interface.
More About Function of PCI Slot
A PCI slot is a built-in slot on a device. It allows for the attachment of various hardware components such as network cards, modems, sound cards, disk controllers and other peripherals. It helped people with do-it-yourself (DIY) projects achieve their goals.
The first original 32-bit, 33 MHz PCI standard supported data transfer rates of 133 megabytes per second. An upgraded 64-bit, 66 MHz standard was introduced later and allowed for much faster data transfer rates up to 533 MHz. IBM, HP, and Compaq introduced PCI-X (or “PCI eXtended”), in 1998. This standard was backwards compatible with PCI. The 133 MHz PCI-X interface supported data transfer rates up to 1064 MHz.
Both PCI and PCI-X were superseded by PCI Express. It was was introduced in the year 2004.
PCI Express
PCI Express (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express), officially abbreviated as PCIe or PCI-e. It is a high-speed serial computer expansion bus standard, designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X and AGP bus standards. It is the common motherboard interface for graphics cards, hard drives, SSDs, Wi-Fi and Ethernet hardware connections on personal computers.
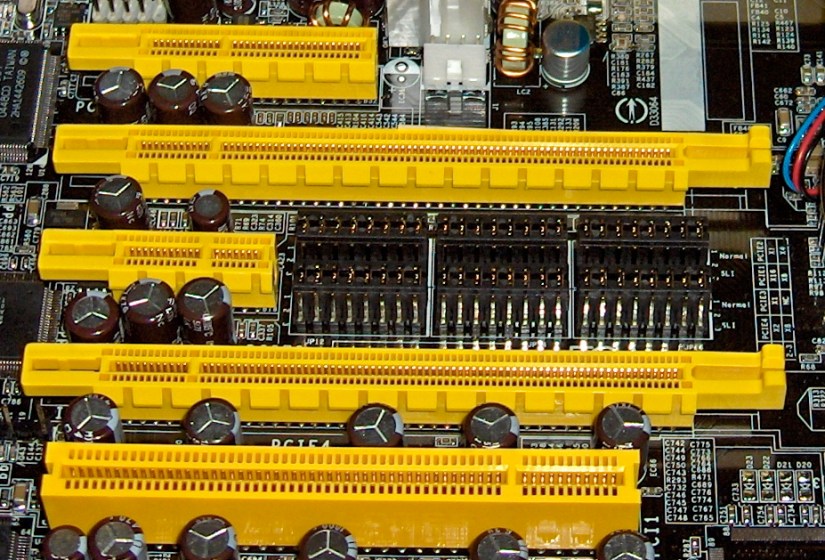
Improvements Over Older Standards
Some of the improvements over the older standards are;
- Higher maximum system bus throughput
- Lower I/O pin count and smaller physical footprint
- Better performance scaling for bus devices
- Detailed error detection and reporting mechanism (Advanced Error Reporting, AER),
- Native hot-swap functionality.
- Recent revisions of the PCIe standard providing hardware support for I/O virtualization.
![]()









![[Resource]: Installing Webuzo on Your Nestict Cloud VPS: A Detailed Guide](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/image.webp)
![[Resource] : Comprehensive List of Equity Bank Codes Across Kenya by Region](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/image-5.png)


![[Continuation]: Current Challenges in Making Physics and Geography Compulsory](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/The-universe-of-mathematics-physic-and-astronomy-its-ama…-Flickr.jpg)
![[Resource] : Why Physics and Geography Should Be Compulsory Like Mathematics in Education](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/image.png)
![[LINKTREE] 2024 PAST PAPERS , NOTES ,RESOURCE,REVISION,EXAMINATIONS](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/SCHM.jpeg)


![Maritime Terms, Abbreviations and Acronyms [Shipping Terms – Searchable]](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/Container-Stowage-Stock-Illustrations-–-71-Container-Stowage-Stock-Illustrations-Vectors-Clipart-Dreamstime.jpg)
![Maritime Terms, Abbreviations and Acronyms [ Shipping Terms]](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/image.png)




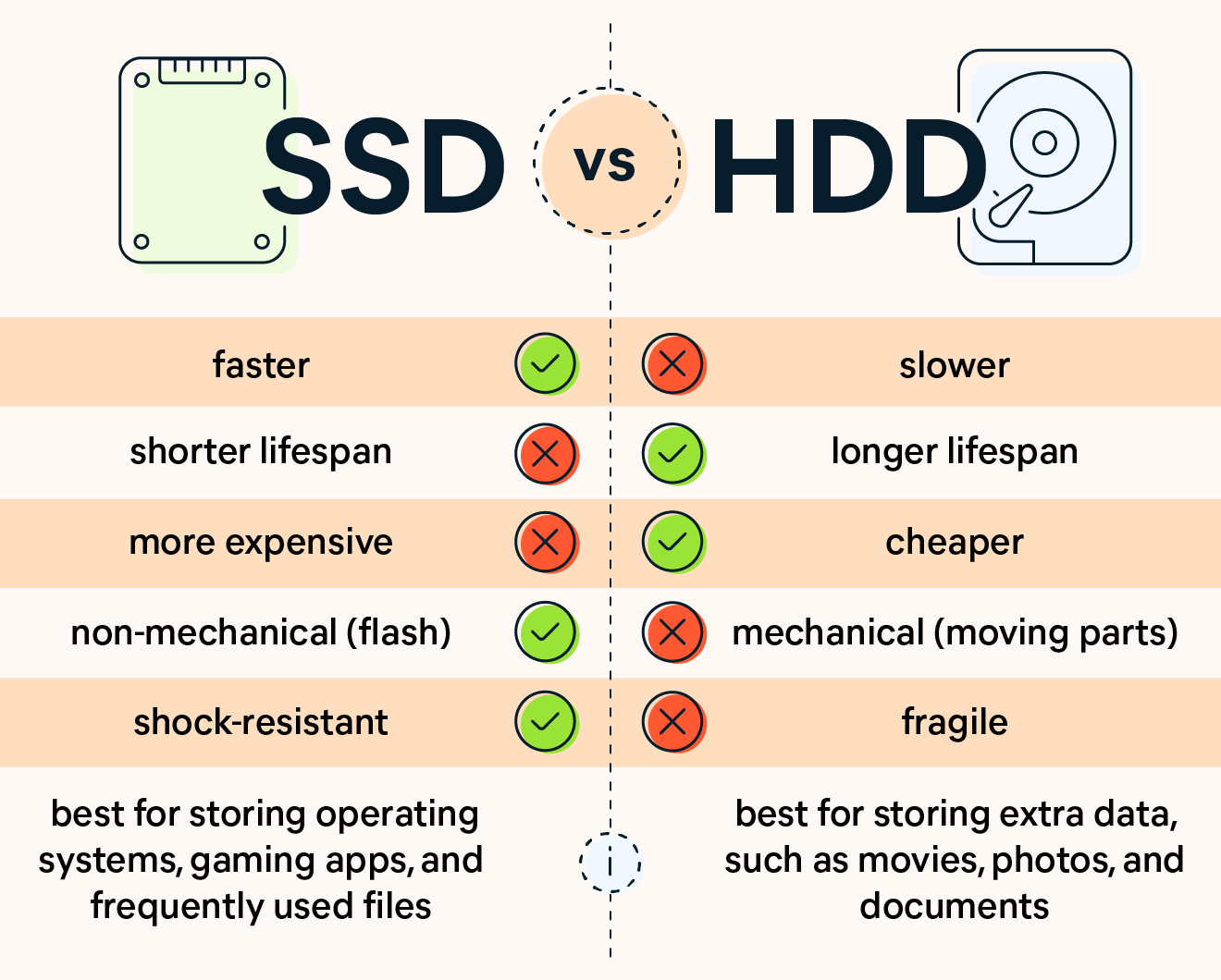
![[Explainer]: NVMe storage, SSD (SATA SSD), and HDD](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Laptops-are-available-with-SSDs-and-HDDs.png)






![[Updated 2024] – Passport Application FOR CHILDREN ONLY(PERSONS UNDER 18 YEARS)](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/keppp-240x172.png)
![[Updated 2024] -Passport Application FOR ADULTS ONLY-PERSONS OVER 18 YEARS](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/EAF-Passport-e1631045054464-400x800-1-240x172.jpg)