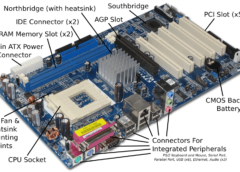
Application Service Provider (ASP) Definition | TLDR
An application service provider (ASP) is a company that hosts and delivers software applications and related services over the internet to customers who access them remotely.
Application Service Provider (ASP) Meaning
An Application Service Provider (ASP) is a business model where a third-party organization hosts and manages software applications and makes them available to customers over the internet. Essentially, ASPs deliver software applications and related services to users via a network, typically the internet, instead of users having to install and maintain the software on their own computers or servers. This model allows users to access the applications they need without the burden of software installation, maintenance, or infrastructure management.
What role does an Application Service Provider (ASP) play in modern software deployment, and what are the key benefits and considerations associated with utilizing ASPs?
· Definition of Application Service Provider (ASP)
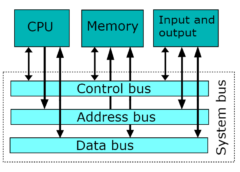
An ASP is a third-party provider that hosts and manages software applications and services on behalf of its clients, delivering them over the Internet or a private network.
· Software Deployment Simplification
ASPs streamline software deployment by eliminating the need for organizations to install, configure, and maintain software on their infrastructure. Instead, clients access the software applications remotely via the Internet, reducing IT overhead and complexity.
· Cost-effectiveness and Scalability
ASPs offer cost-effective solutions as clients typically pay subscription fees or usage-based charges, avoiding upfront capital investments in software licenses and hardware infrastructure. Additionally, ASPs often provide scalable solutions, allowing clients to adjust their usage levels and expand or contract services as needed.
· Enhanced Accessibility and Collaboration
By hosting applications in the cloud, ASPs enable users to access software and collaborate from anywhere with internet connectivity. This enhances productivity and facilitates remote work scenarios, especially in today’s distributed and globalized business environments.
· Security and Data Privacy Considerations
While ASPs offer numerous benefits, organizations must carefully consider security and data privacy implications. Entrusting sensitive data to third-party providers requires robust security measures and contractual agreements to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, and compliance with regulatory requirements. Organizations need to evaluate the security practices and certifications of ASPs before engaging in their services.
70 total views , 1 views today
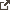









![[Resource]: Installing Webuzo on Your Nestict Cloud VPS: A Detailed Guide](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/image.webp)
![[Resource] : Comprehensive List of Equity Bank Codes Across Kenya by Region](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/image-5.png)


![[Continuation]: Current Challenges in Making Physics and Geography Compulsory](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/The-universe-of-mathematics-physic-and-astronomy-its-ama…-Flickr.jpg)
![[Resource] : Why Physics and Geography Should Be Compulsory Like Mathematics in Education](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/image.png)
![[LINKTREE] 2024 PAST PAPERS , NOTES ,RESOURCE,REVISION,EXAMINATIONS](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/10/SCHM.jpeg)


![Maritime Terms, Abbreviations and Acronyms [Shipping Terms – Searchable]](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/Container-Stowage-Stock-Illustrations-–-71-Container-Stowage-Stock-Illustrations-Vectors-Clipart-Dreamstime.jpg)
![Maritime Terms, Abbreviations and Acronyms [ Shipping Terms]](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/09/image.png)




![[Explainer]: NVMe storage, SSD (SATA SSD), and HDD](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/08/Laptops-are-available-with-SSDs-and-HDDs.png)





![[Updated 2024] – Passport Application FOR CHILDREN ONLY(PERSONS UNDER 18 YEARS)](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/keppp-240x172.png)
![[Updated 2024] -Passport Application FOR ADULTS ONLY-PERSONS OVER 18 YEARS](https://www.blog.nestict.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/09/EAF-Passport-e1631045054464-400x800-1-240x172.jpg)